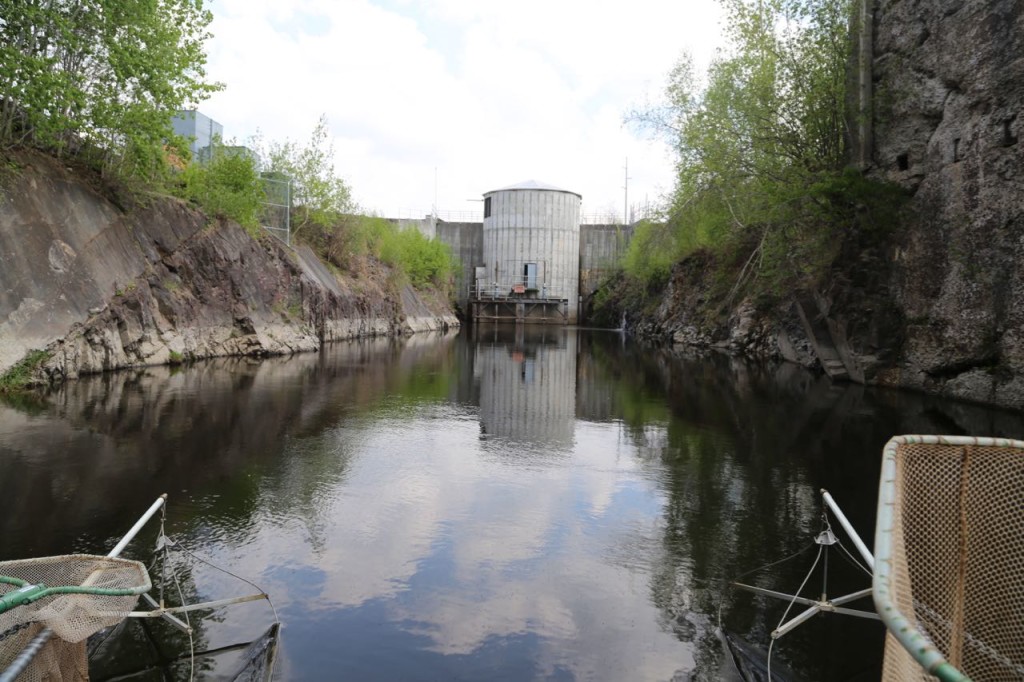
Recently for work I got to help out in the field taking samples to quantify environmental contamination. Some of the samples we were taking were fish tissue to measure the levels of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) in them. The fish live in a river that was contaminated decades ago. The sampling results will be used for fish advisories and also to determine a clean up plan.
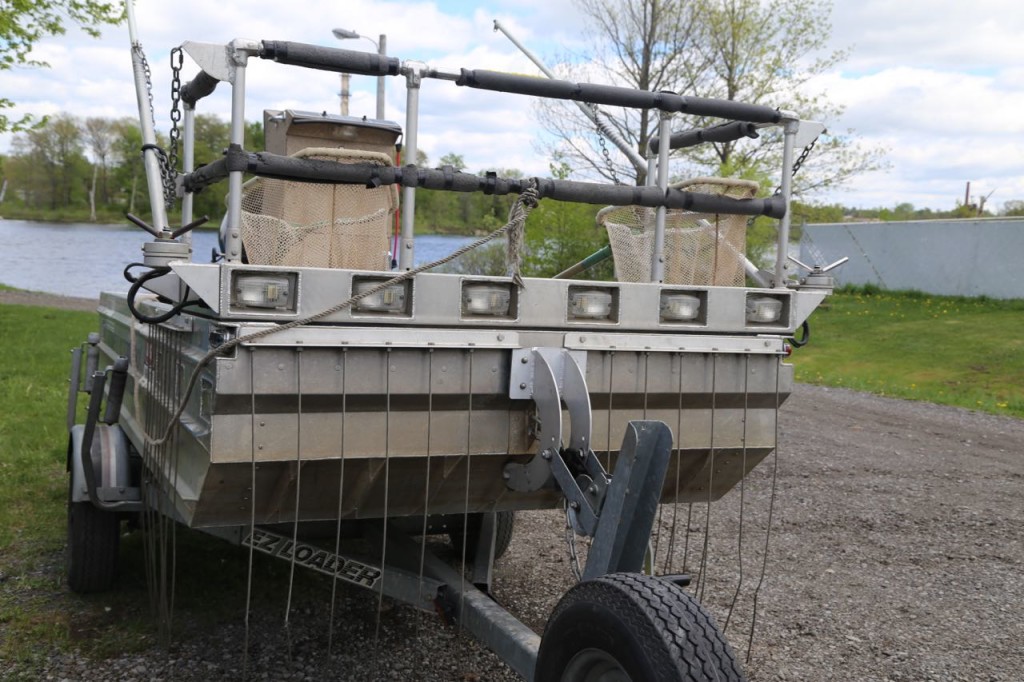
Sampling fish starts with the really fun part, which is cruising on a small electrofishing boat. Electroshocking the fish allows you to catch them alive and throw back any fish we didn’t want. We had target fish we were trying to catch to sample, and those were the only ones we kept, and we only the number of target fish we needed. The electroshock sort of stuns the fish but doesn’t kill them. The electrofishing boat has two long poles with anode wires hanging off of them protruding from the front of the boat. There were more wires hanging from the bow of the boat, and those are the cathodes. The electricity flows from the anodes to the cathodes. We stood at the front of the boat in rubber soled boots with nets extended waiting to catch any fish stunned by the electroshocking. Netting electroshocked fish is not actually as easy as it sounds. Some of the fish are more stunned than others, so some fish seem slightly confused but then swim away. Also, some were stunned but at a depth too low or cloudy for us to catch or see. According to the boat’s captain, the water had really low conductivity, which was making it difficult. Since we had target fish we were trying to catch, I, naturally, kept catching fish we didn’t want. I threw a lot of fish back. Still, a day on a boat catching or not catching fish was a wonderful change from the cubical I normally work in. Also, I learned that you really need polarized sunglasses when out on the water.
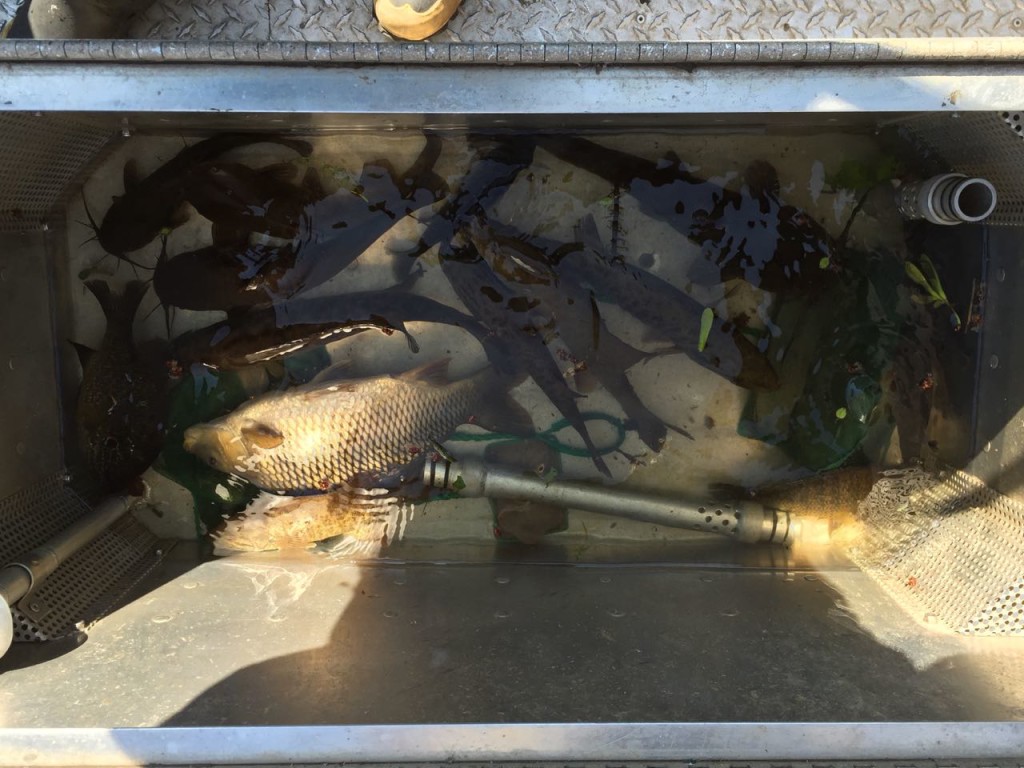
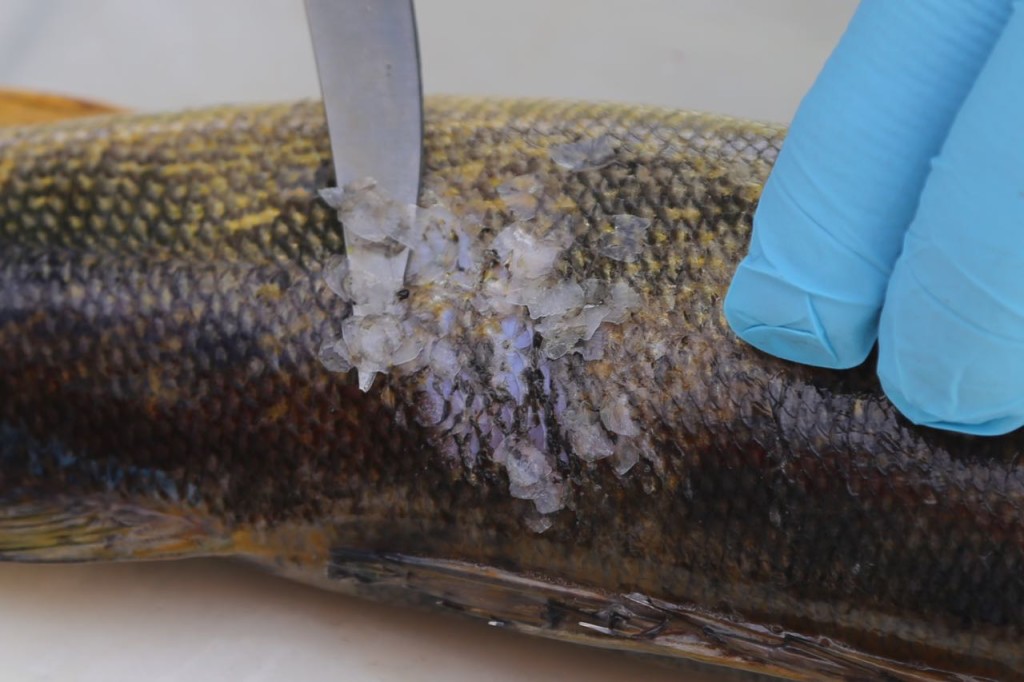
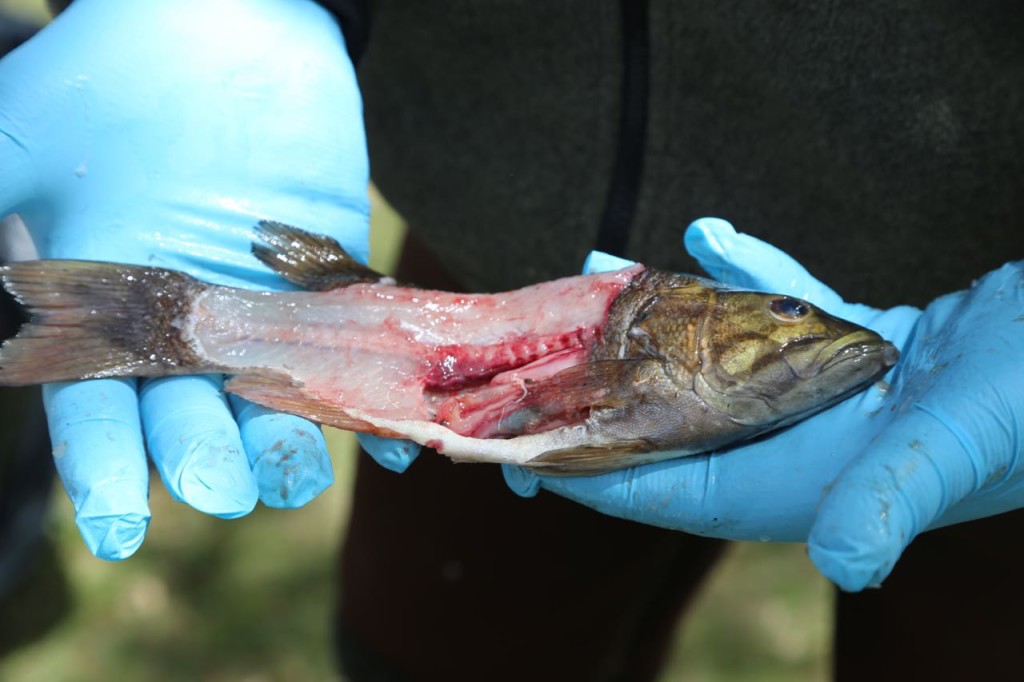
Once we got the fish to shore, the biologist took over. The fish were weighed and their length measured. He took a a sample of their scales from a standard location, and those scales were going to be used by a laboratory to determine their age. Evidently scales can be used to age fish in the same manner tree rings age trees. WARNING: If you are uncomfortable looking at the insides of fish, do not read any further. You should probably not eat fish also, if you can’t look at an uncooked one.
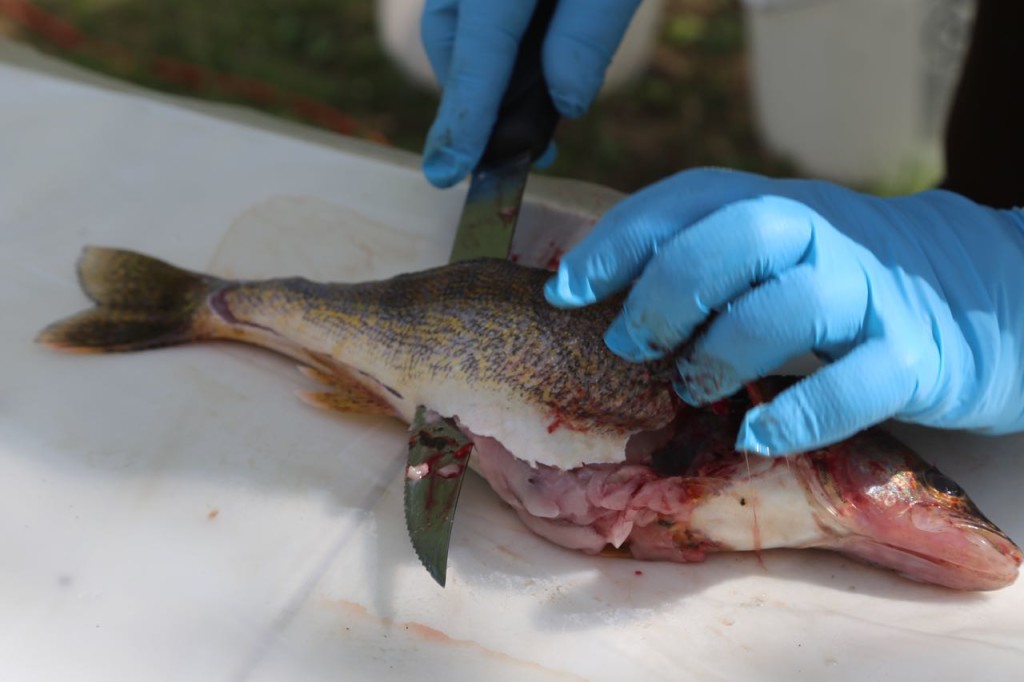
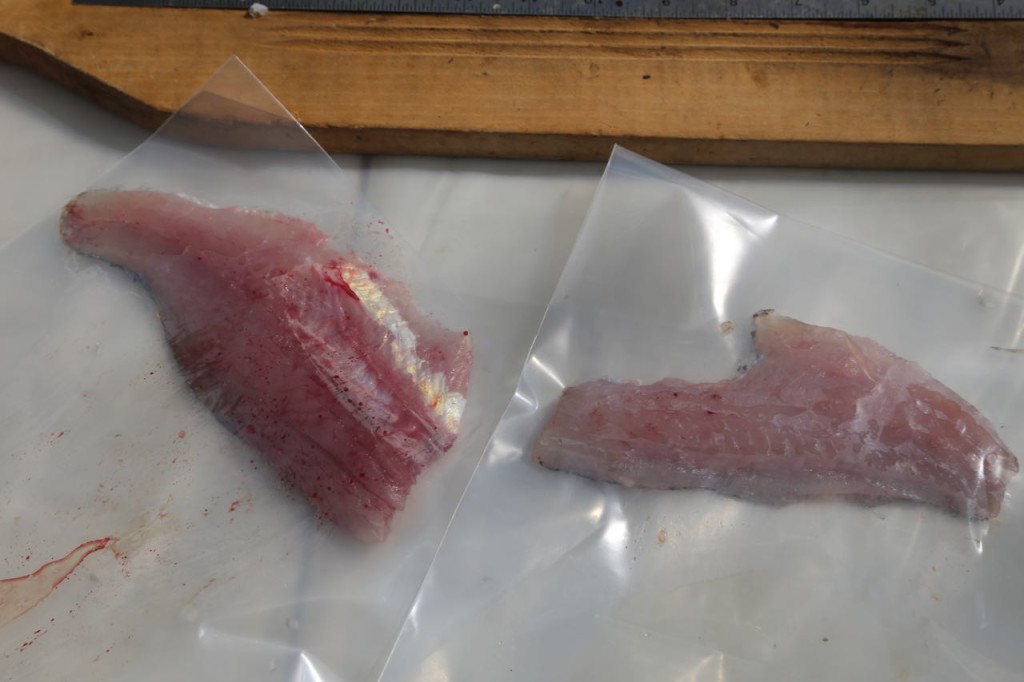
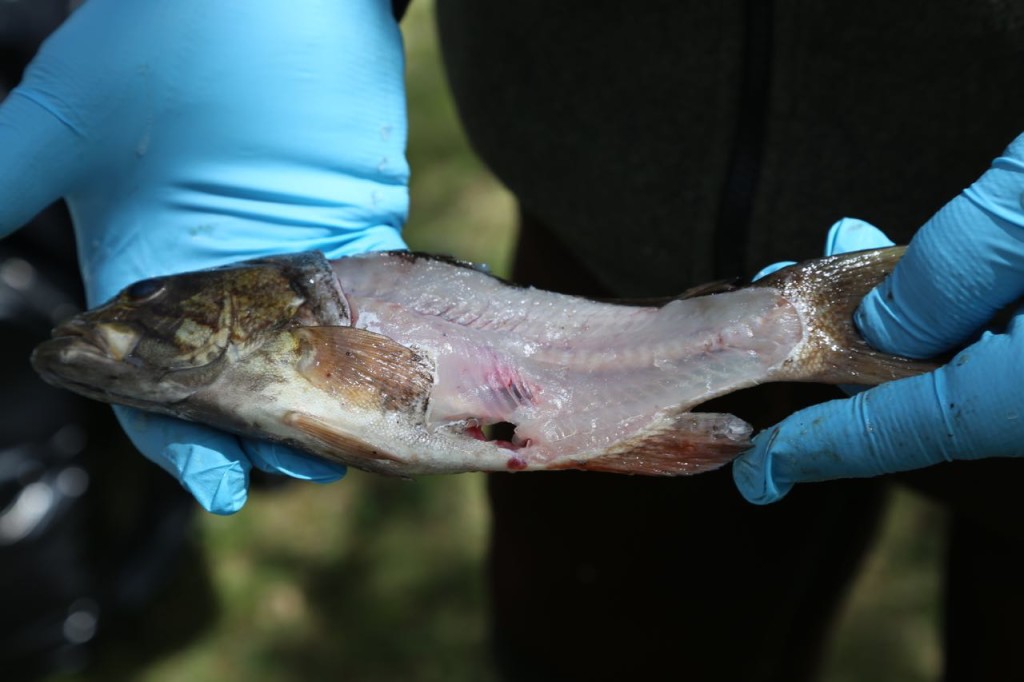
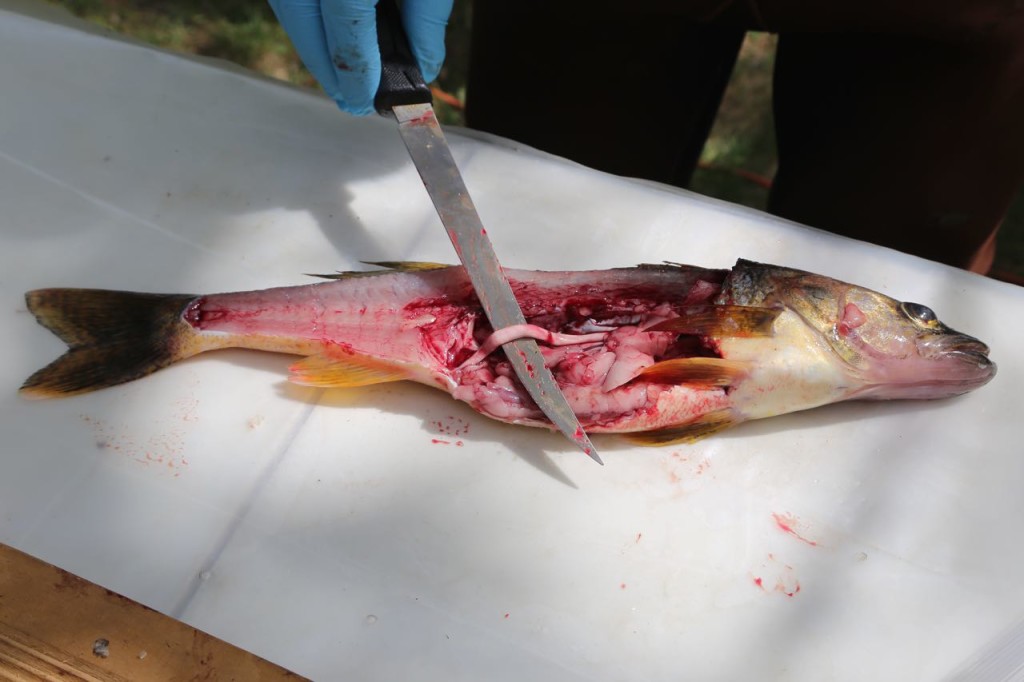
The rest of the scales were then scraped off. The fish were then cut. Only the fillets were used for sampling. The part of the fish used for sampling can differ depending on what the exposure pathway being examined is. We took two different parts: the filet, which represents what a human would normally eat, and also the fillet with rib meat. The rib meat is normally not eaten, but it would have more PCBs in it, so using it in the sample would represent a worse case scenario for a human consuming fish.
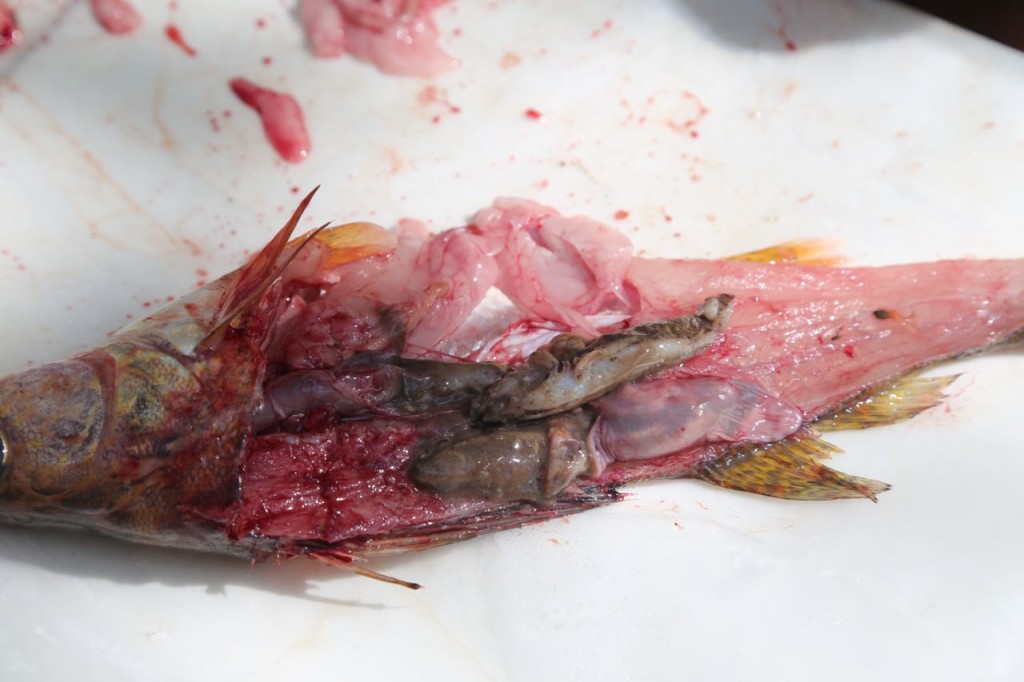
I also learned a bit of fish anatomy during the sampling. The biologist was also sexing the fish.
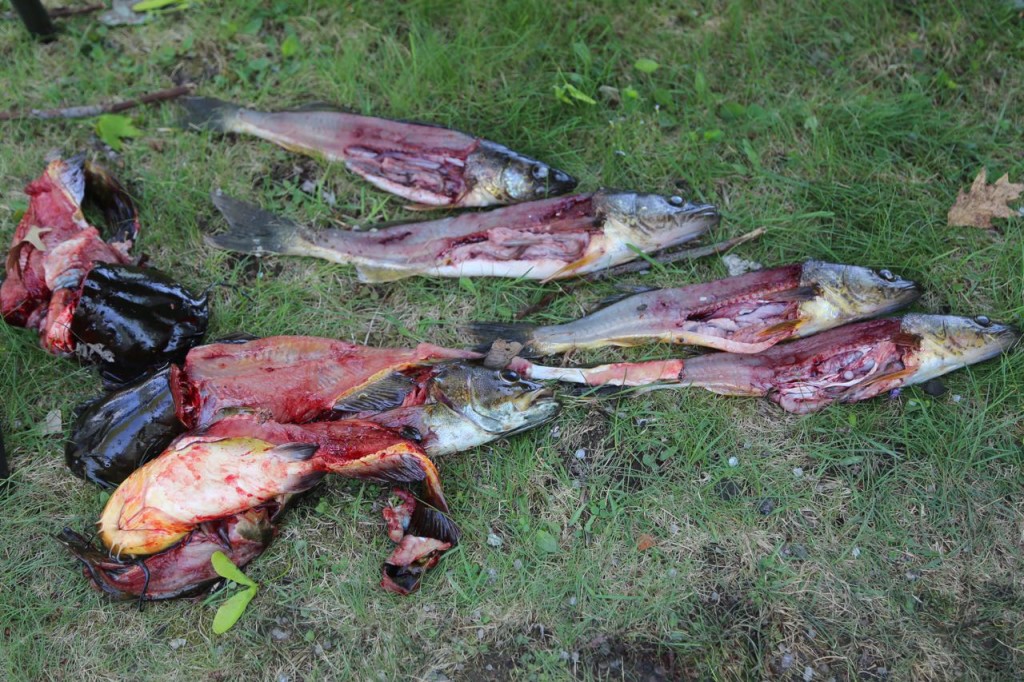
We weren’t necropsying the fish, but we still got a look inside, including sometimes as to what it had eaten recently.
We sampled quite a few fish, but it was for science and to benefit the community.