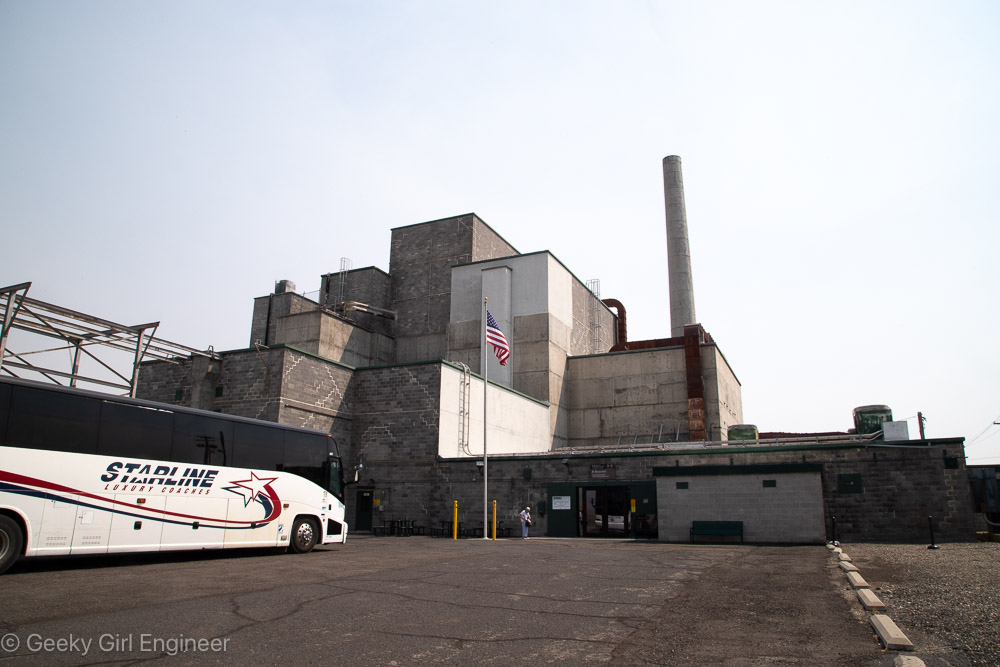
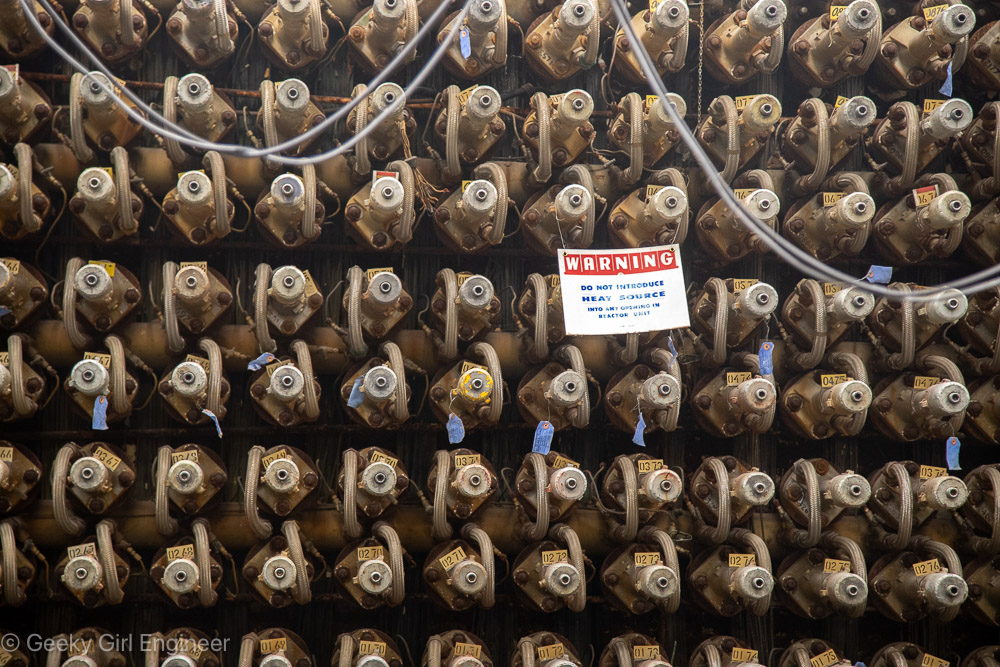
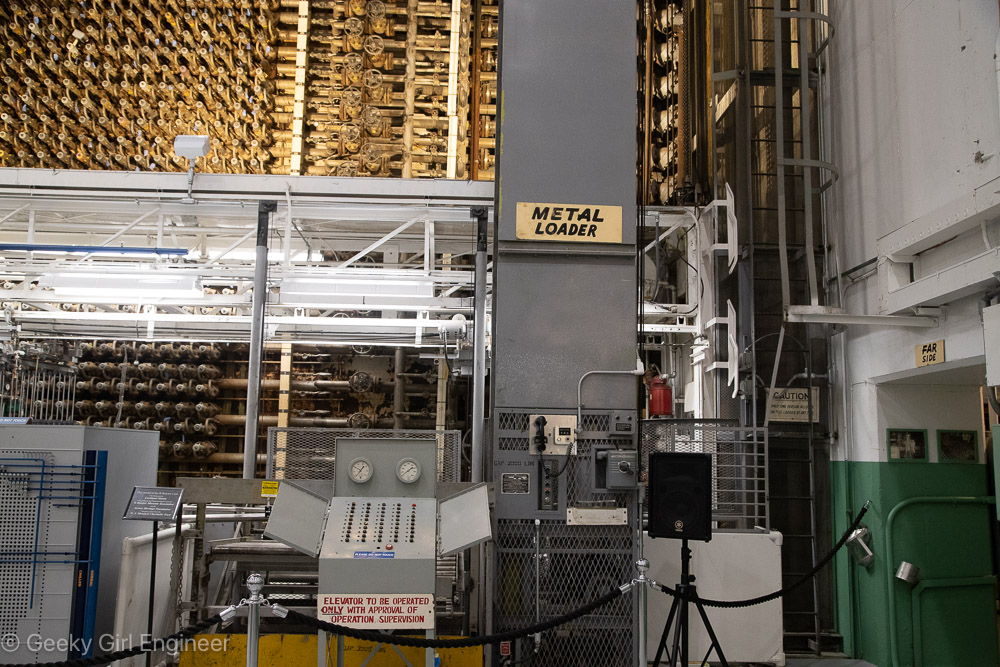
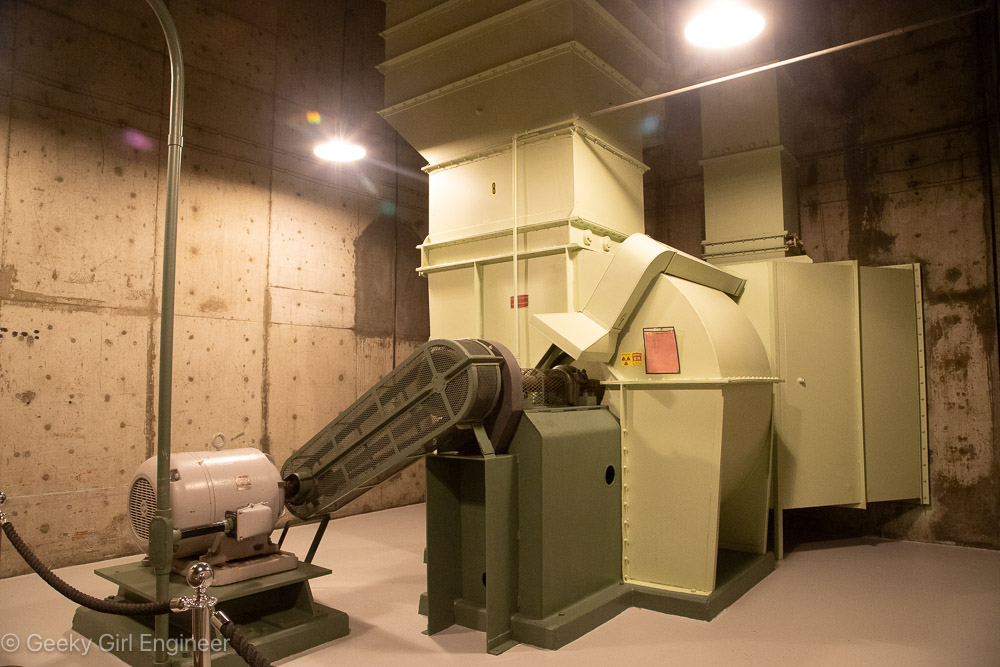
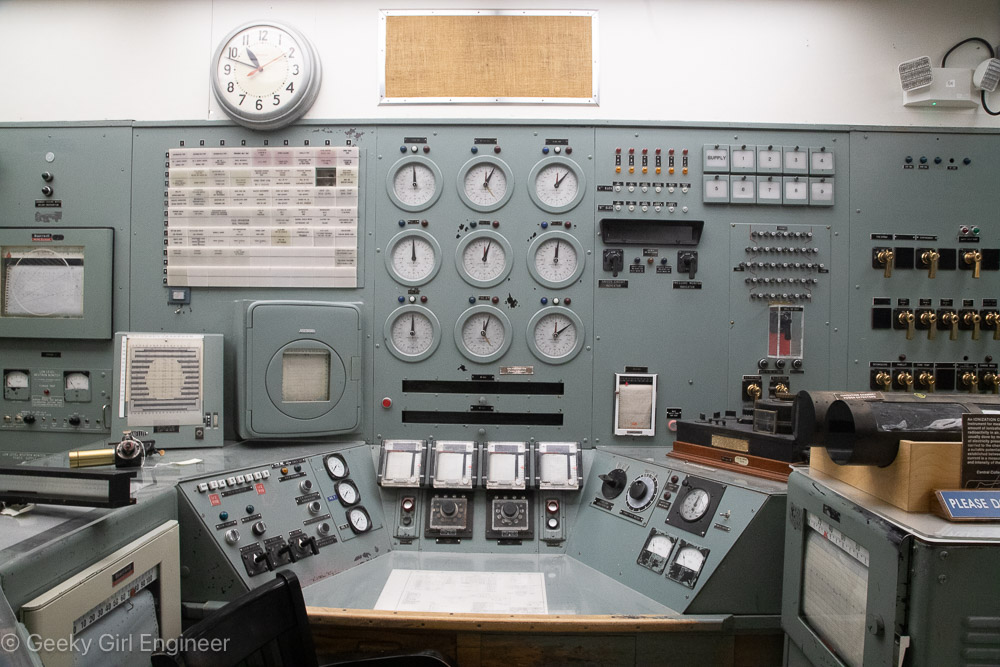
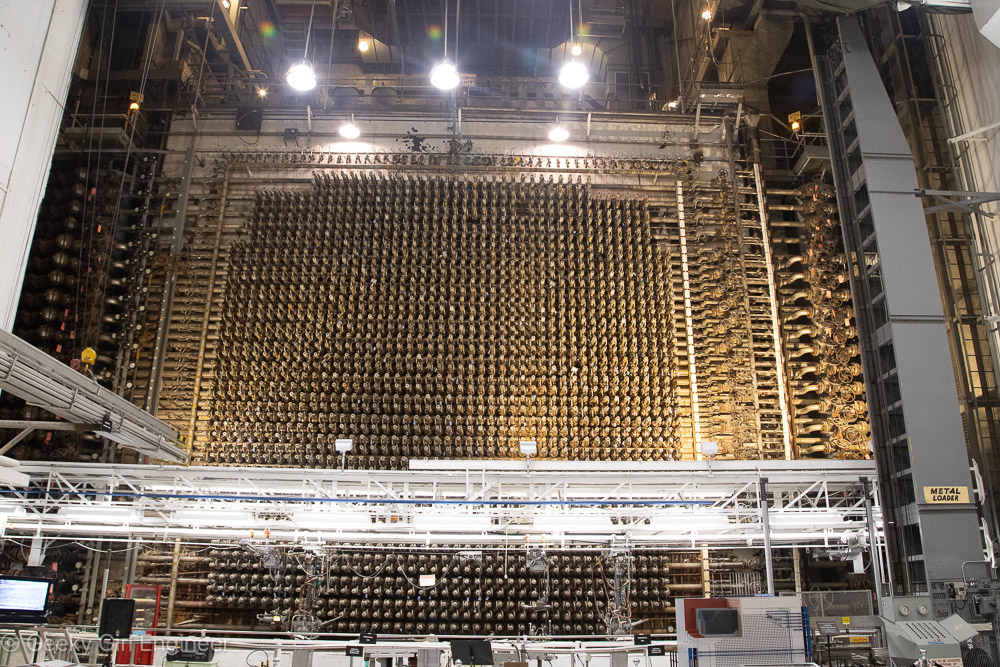
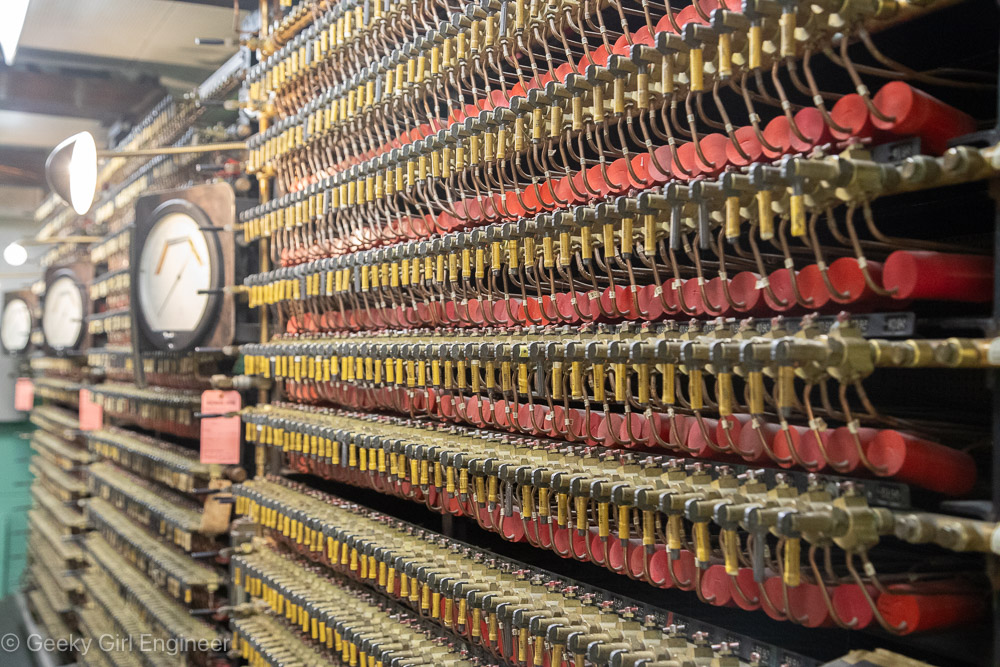
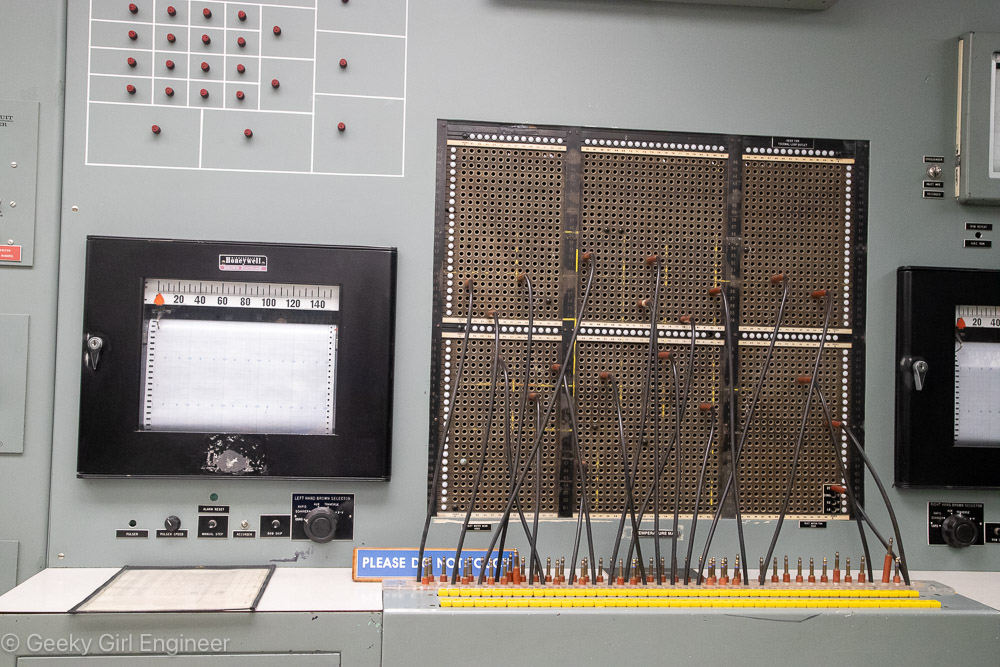
Yesterday I went on what is pretty much a nerd tour of Hanford Reactor B. Hanford is the Department of Energy facility where they made plutonium to make nuclear bombs, and Reactor B was the first reactor built during World War II to make plutonium. It is now a National Historic Landmark. The tour included a long bus ride to the site, which gives you a better understanding of just how big Hanford is. The tour then includes several hours to wander around the building, and several presentations by docents. I still can’t quite get over the fact that the public can tour a building where they used to make plutonium, which is rather radioactive and toxic.
The science and engineering behind the facility was impressive, and I also enjoyed looking at 1940s era technology and signage. I don’t if it was that era, or the facility, or what, but there were some fun signs all over the place. There were also some hidden historical signs, like all the clocks were stopped at 10:48, which was time on the night of September 26, 1944 when the reactor achieved fission for the first time. I don’t know why, but I was amused that almost every room had a “broom” station, which were pegs on the wall where a broom and dustpan were hung. I think I only saw one room where there was actually a broom in its proper station. I guess they do less sweeping now, or they have moved onto vacuum technology.
I really appreciated that you could wander around and spend your time looking at everything. Most of the areas have decent signage to indicate what you are looking at, although the engineer that I am, I would prefer perhaps a bit more detail. My one criticism of the tour was that they completed glossed over the amount of environmental contamination created at Hanford. In an intro video we watched before taking the tour, they briefly mention that waste was buried to be dealt with later. The docent at one point said they are cleaning up the site, which is an understatement. I know enough about the site to feel like they just didn’t want to admit the contamination they caused. Signs of remediation are present in the building. There were plenty of pipes that obviously had asbestos, and the pipes had clearly been abated to encapsulate the asbestos, so it would not become airborne and thus a hazard. There were dosimeters on the walls everywhere, which were clearly been analyzed frequently.
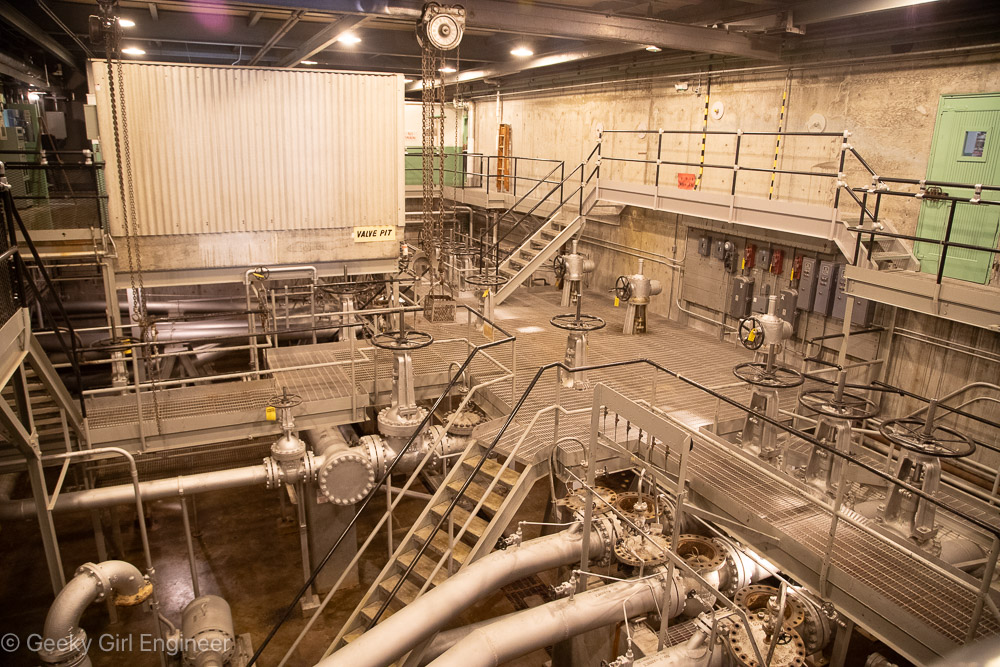

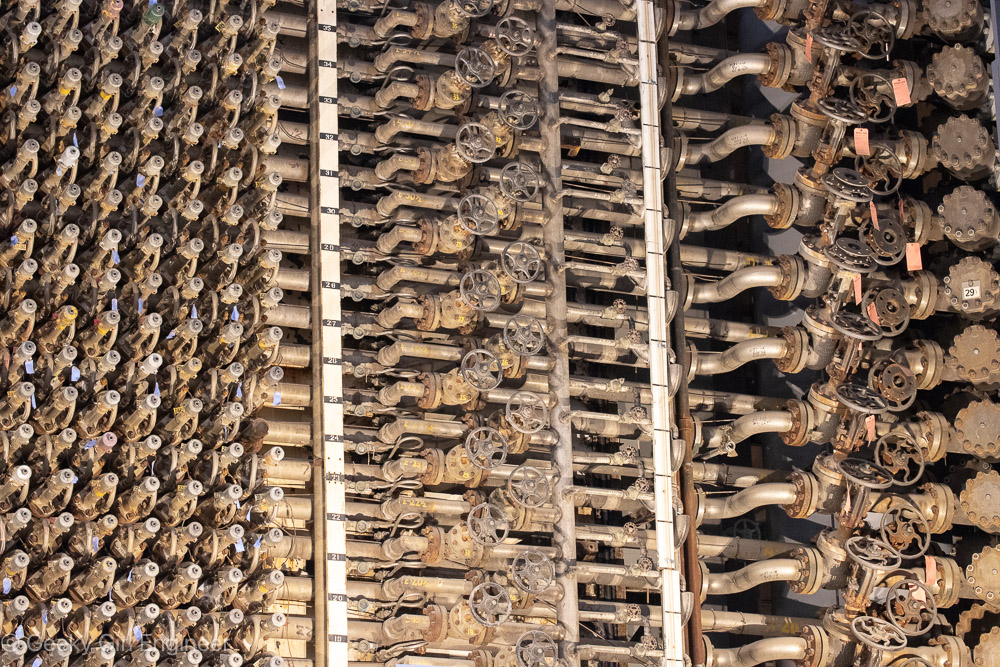
Valve Pit Room; notice in lower right, tops have been removed from access openings; tops were removed at Russian inspectors’ request to prove no water was going through pipes as part of treaty to reduce nuclear weapons